For the Agariyas
Sustainable Salt Farming using Solar PV Systems





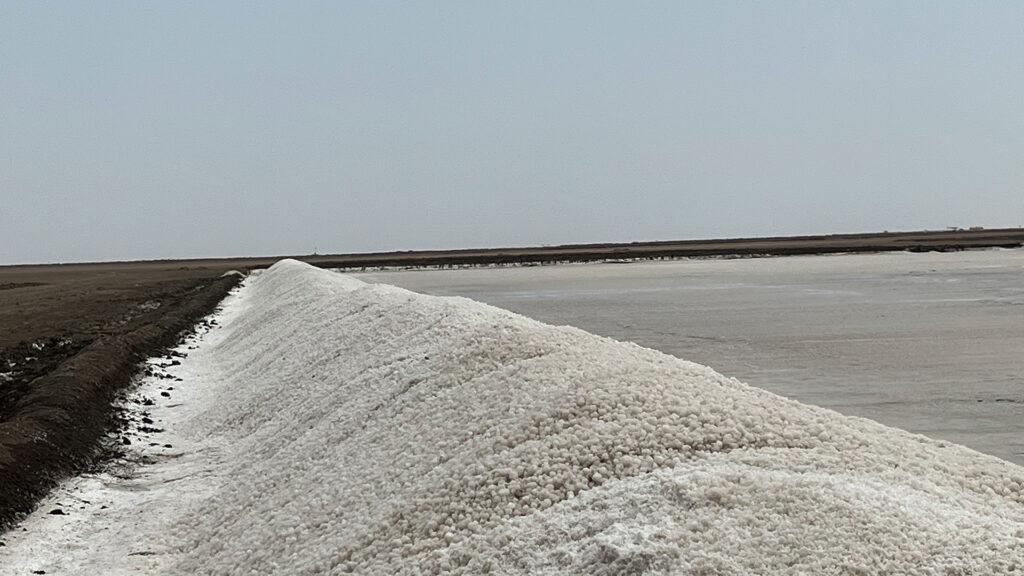
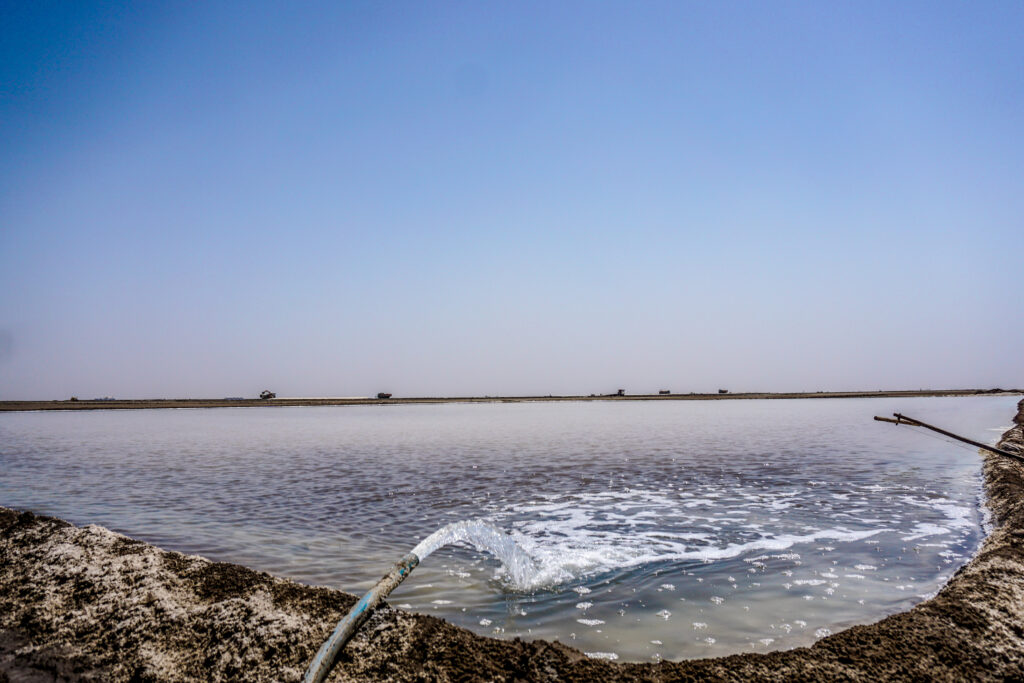
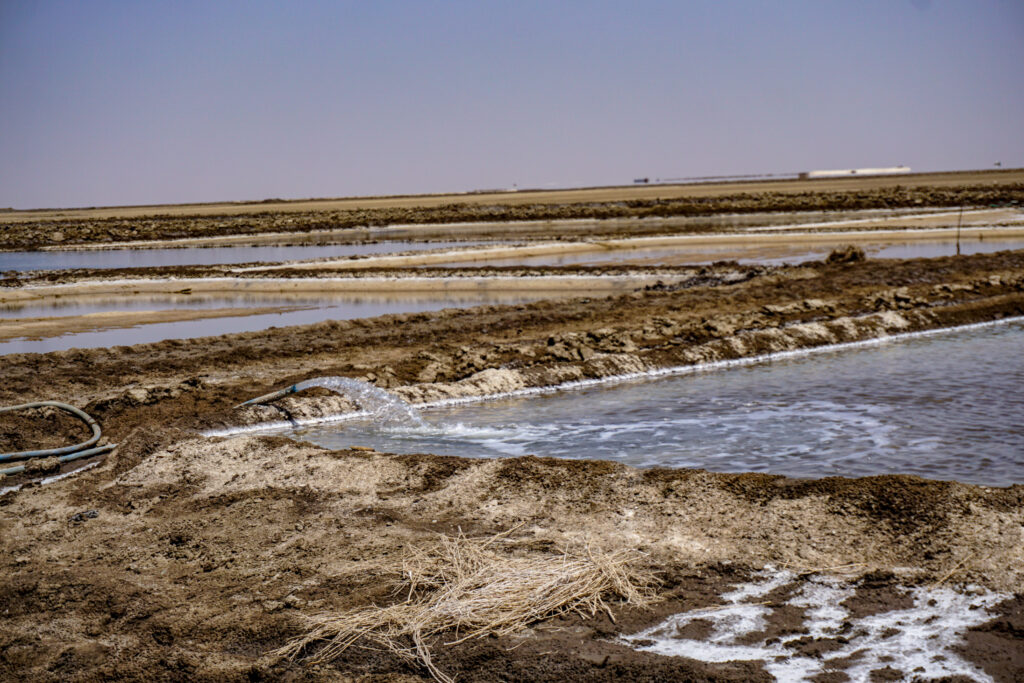
In the Rann of Kutch, India’s premier salt-producing region contributing over 75% of the nation’s output, a transformative solar-powered water pump initiative is changing traditional salt farming practices. This strategic approach replaces conventional diesel pumps with solar photovoltaic (PV) panels, providing a cost-effective energy solution for extracting brine from subterranean and surface sources. The Gujarat Solar Project results in emission reduction and encourages the adoption of renewable energy to improve the Agariyas’ (salt farmers) livelihood.
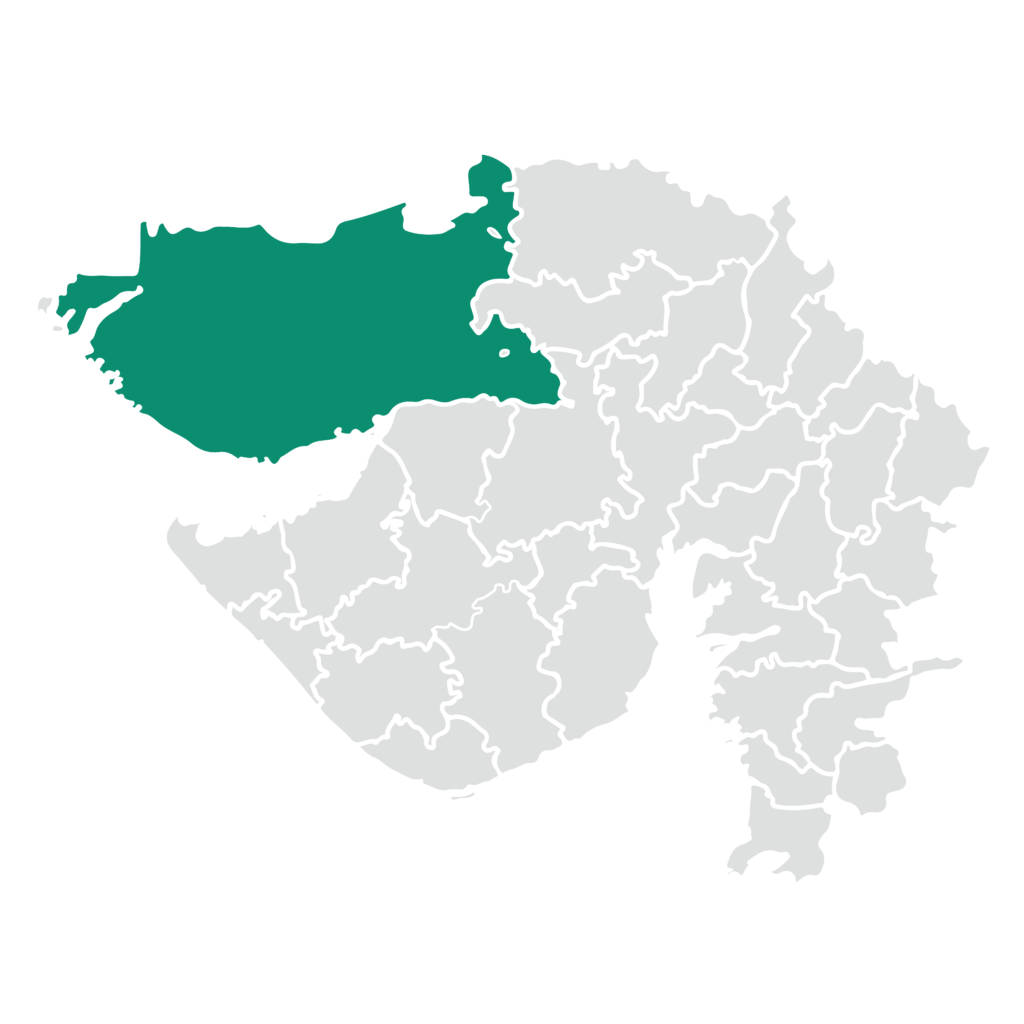
Kutch – Gujarat
Project Location: Kutch region of Gujarat, India
Methodology: Mechanical energy for the user with or without electrical energy
Standard: Gold Standard
Total Project Area: 5,450 Hectares
Villages: 1,588
Country: India
Installed: 1,292 solar PV arrays
Deployment Plan: 1,600 solar PV arrays
Solar Water Pumps Advancing Women’s Livelihoods
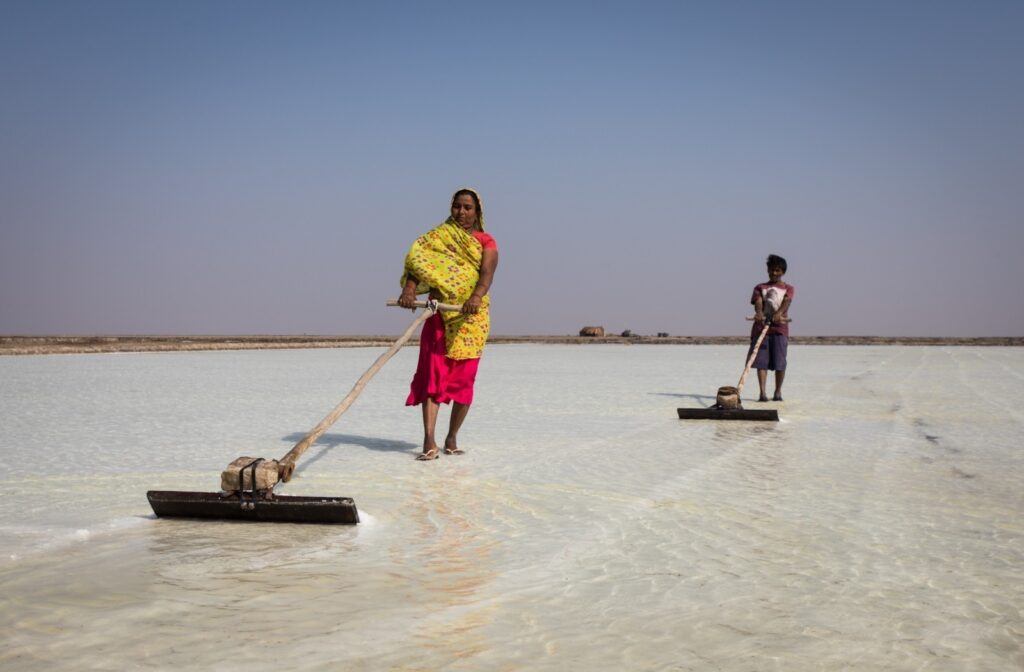
At the heart of the initiative is the well-being of women workers, who constitute most of the unorganized salt farming workforce. Through strategic subsidization of solar-powered water pumps, the project enables reliable energy access while significantly reducing operational costs associated with diesel consumption. This decentralized energy solution enable the Agariyas to optimize their brine collection processes, creating a sustainable pathway to improved economic outcomes and community resilience.






The transition to solar PV technology marks a significant improvement in workplace safety conditions. By eliminating diesel-powered pumps, the initiative removes harmful exhaust fumes from salt pan work areas, creating a healthier working environment for salt farmers. This technological shift demonstrates how renewable energy adoption can directly contribute to worker well-being and occupational safety.
The project implements a comprehensive approach to women’s meaningful participation through structured capacity-building initiatives and leadership development programs. By focusing on women in the unorganized sector, the initiative creates pathways to self-reliance and enhanced income security. The substantial cost savings from solar-powered operations translate directly into improved livelihoods, demonstrating the interconnection between technological advancement and social progress.
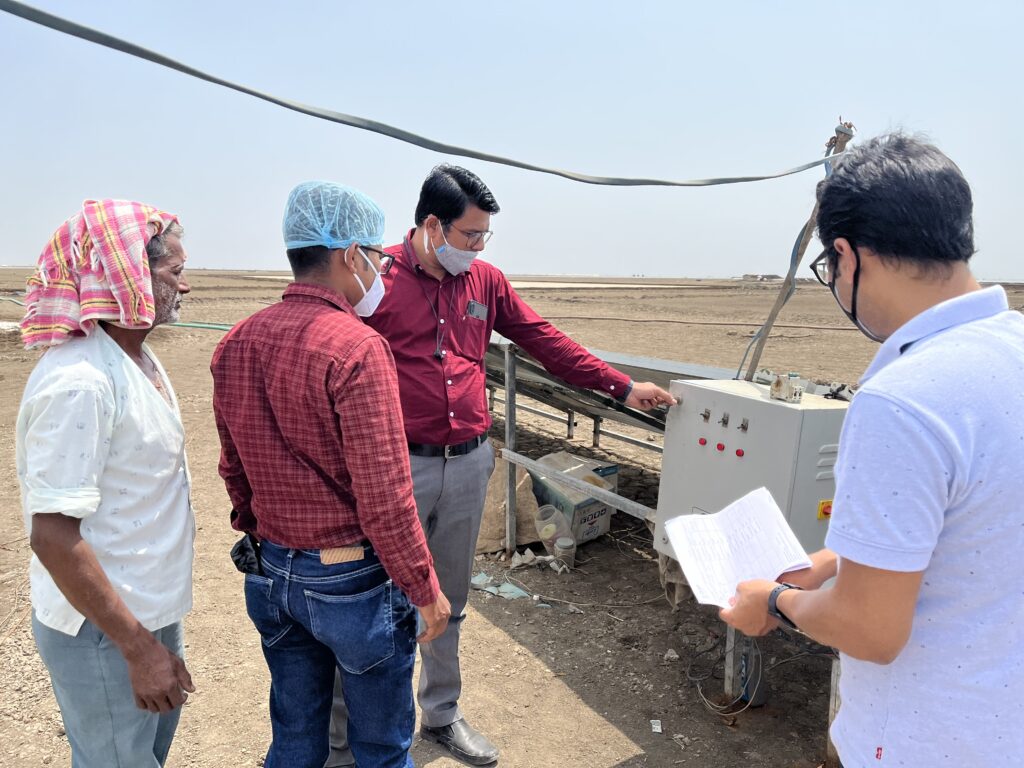
Through the strategic deployment of solar PV systems for pump operations, the initiative establishes reliable and affordable clean energy infrastructure crucial to salt farming operations. This technological transition fundamentally transforms the Agariyas’ production capabilities, directly impacting their food security and quality of life. The project demonstrates how renewable energy access can catalyze broader community development.
The initiative achieves remarkable efficiency gains, eliminating approximately 1,600 liters of diesel consumption annually per installation. This substantial reduction in fuel dependency translates directly into financial savings for salt farming communities. The project creates a sustainable economic growth model by ensuring continuous employment opportunities, particularly for women salt farmers, while generating significant cost savings through reduced diesel dependency.
The project’s environmental impact is substantial, with the replacement of 700 diesel pumps with solar alternatives in its inaugural year, resulting in annual carbon dioxide emission reductions exceeding 3,000 tonnes. This technological transition demonstrates the significant potential for emissions reduction through targeted renewable energy adoption in agricultural operations.
Occupational Health Enhancement

The transition to solar PV technology marks a significant improvement in workplace safety conditions. By eliminating diesel-powered pumps, the initiative removes harmful exhaust fumes from salt pan work areas, creating a healthier working environment for salt farmers. This technological shift demonstrates how renewable energy adoption can directly contribute to worker well-being and occupational safety.
Improving Livelihood

The project implements a comprehensive approach to women’s meaningful participation through structured capacity-building initiatives and leadership development programs. By focusing on women in the unorganized sector, the initiative creates pathways to self-reliance and enhanced income security. The substantial cost savings from solar-powered operations translate directly into improved livelihoods, demonstrating the interconnection between technological advancement and social progress.
Sustainable Energy Access

Through the strategic deployment of solar PV systems for pump operations, the initiative establishes reliable and affordable clean energy infrastructure crucial to salt farming operations. This technological transition fundamentally transforms the Agariyas’ production capabilities, directly impacting their food security and quality of life. The project demonstrates how renewable energy access can catalyze broader community development.Through the strategic deployment of solar PV systems for pump operations, the initiative establishes reliable and affordable clean energy infrastructure crucial to salt farming operations. This technological transition fundamentally transforms the Agariyas’ production capabilities, directly impacting their food security and quality of life. The project demonstrates how renewable energy access can catalyze broader community development.
Economic Enhancement

The initiative achieves remarkable efficiency gains, eliminating approximately 1,600 liters of diesel consumption annually per installation. This substantial reduction in fuel dependency translates directly into financial savings for salt farming communities. The project creates a sustainable economic growth model by ensuring continuous employment opportunities, particularly for women salt farmers, while generating significant cost savings through reduced diesel dependency.The initiative achieves remarkable efficiency gains, eliminating approximately 1,600 liters of diesel consumption annually per installation. This substantial reduction in fuel dependency translates directly into financial savings for salt farming communities. The project creates a sustainable economic growth model by ensuring continuous employment opportunities, particularly for women salt farmers, while generating significant cost savings through reduced diesel dependency.
Climate Action

The project’s environmental impact is substantial, with the replacement of 700 diesel pumps with solar alternatives in its inaugural year, resulting in annual carbon dioxide emission reductions exceeding 3,000 tonnes. This technological transition demonstrates the significant potential for emissions reduction through targeted renewable energy adoption in agricultural operations.The project’s environmental impact is substantial, with the replacement of 700 diesel pumps with solar alternatives in its inaugural year, resulting in annual carbon dioxide emission reductions exceeding 3,000 tonnes. This technological transition demonstrates the significant potential for emissions reduction through targeted renewable energy adoption in agricultural operations.
Gallery